This beginner's guide explains the main types of DNS records used when pointing a domain to a web host. Understanding these core concepts will allow you to get your website live with the proper domain-to-hosting connections in place.
What are DNS Records?
DNS records allow you to route your domain name to connect with your web hosting provider's servers.
If you have a VPS, you will want to point your domain A records to the server IP:
A Records
A records point your domain to the IP address of your web host's server that stores your website files. This connects your domain to their servers.
See following article for more information.
If you have shared hosting, you will want to point your domain to the hosting NS records:
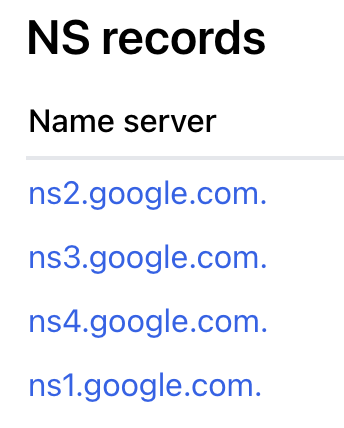
NS Records
NS (name server) records link your domain to the nameservers used by your web hosting company. This gives them control to manage your DNS records. Upon a website hosting order purchase, NS records are sent via email.
Example image:
CNAME Records
A CNAME creates an alias for your root domain name. For example, you can use a CNAME to point "www.yourdomain.com" to "yourdomain.com".
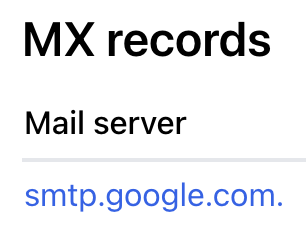
MX Records
MX records designate the mail server that should receive all emails for your domain's email addresses, routing messages to your inbox.
DNS Servers
DNS records are stored in DNS servers around the world that maintain directories linking domains to corresponding IPs.
Propagation Delays
When you purchase hosting, your provider gives you the nameservers and IP address details to use when setting up your DNS records. It can take up to 48 hours for DNS changes to fully propagate after updating records.
DNS Management Services
Using a service like Cloudflare provides easy management of DNS records through one dashboard. Cloudflare also offers additional security benefits like DDoS protection, bot mitigation, malware scanning and more to keep your site safe from threats. The service sits between your hosting provider and end users to monitor and optimize traffic flow.
Avoiding Errors
Just be cautious of typos when entering DNS details since small errors can break connectivity. Double-check records for accuracy before saving changes.
Configuring DNS records correctly is crucial for directing your domain name to your hosting provider and getting your website online.

